Wei-Chiang Shen
University of Southern California, USA
Title: Human growth hormone–single-chain Fc-dimer fusion protein
Biography
Biography: Wei-Chiang Shen
Abstract
During the past decades, many Fc fusion proteins have been successfully produced by biotech companies and approved by FDA to be used as long-acting forms of protein drug. However, there are several limitations on the application of Fc-fusion protein technology to many proteins, especially the stability of Fc-dimerization. In this report, we describe a novel Fc-based drug carrier, single chain Fc-dimer (sc(Fc)2), which was designed to contain two Fc domains recombinantly linked together via a flexible linker. Since the Fc dimeric structure is maintained through the flexible linker, the hinge region was omitted to further stabilize it against proteolysis and to reduce Fc R-related effector functions. Our results indicate that the recombinant sc(Fc)2 preserved the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binding capacity. We have prepared a fusion protein consisting human growth hormone (hGH) and sc(Fc)2 as a model of the novel Fc fusion protein. Compared to the monomeric hGH-Fc fusion protein, hGH-sc(Fc)2 fusion protein showed a stronger binding affinity to FcRn, a longer in vivo plasma half-life of hGH, and a higher hGH-induced plasma IGF-1 level in mice. Our results suggest that sc(Fc)2 technology has the potential to greatly advance and expand the use of Fc-technology for improving the pharmacokinetics and bioactivity of protein therapeutics
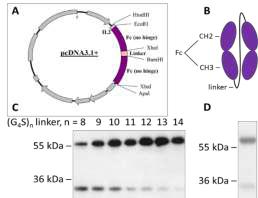
Figure : Production of single-chain Fc-dimer, sc(Fc)2, in HEK 293 cells. (A) Plasmid of sc(Fc)2 expression, (B) Structure of sc(Fc)2, (C) Anti-Fc WB (non-reducing conditions) of sc(Fc)2 with indicated (G4S) linker lengths. (D) Coomassie Blue gel (reducing conditions) of sc(Fc)_(G4S)13.