Felix-Martin Werner
Euro Academy Pößneck, Germany
Title: Treatment of extrapyramidal symptoms in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs
Biography
Biography: Felix-Martin Werner
Abstract
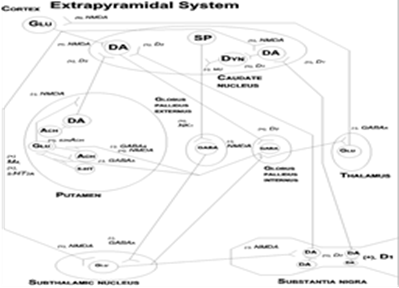
Extrapyramidal symptoms, for example dyskinesia, parkinsonism, akathisia or dystonia can occur in schizophrenic or schizoaffective patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Second-generations antipsychotic drugs such as risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine mostly are D2 and 5-HT2A antagonists and can cause these movement disturbances as a consequence of the D2 receptor blockade. In the mesolimbic system, the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus, dopamine and serotonin hyperactivity and GABA and glutamate hypoactivity are induced by susceptibility genes found in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. The function of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides in the extrapyramidal system are reviewed. Neural networks in the extrapyramidal system and the mesolimbic system are described. In the extrapyramidal system, the neurotransmitter balance between D2 dopaminergic and muscarinic cholinergic neurons and between presynaptic GABAergic and excitotoxic glutamatergic neurons is altered by the second-generation antipsychotic drugs. Possible treatments of extrapyramidal symptoms induced by antipsychotic drugs are M4 antagonists, GABAA agonists and NMDA antagonists. The adverse effects of these additional drugs are presented. Some new antipsychotic drugs such as aripiprazole and cariprazine less often and to a lesser extent cause extrapyramidal symptoms, because they have a partial agonism at the D2 receptor.